
 Menu
Menu
|
School University |

|
||
|
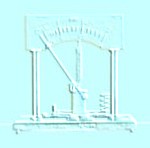
Function To measure the intensity of current and the difference of potential. | |||
|
|||
|
Description It is a moving coil instrument of great sensibility, assembled vertically on a mahogany table. On the basis there are the binding posts, the additional resistance, the parallel resistance and the plug inverter of these resistances. We can use it as a sensitive galvanometer of 200-0-200 mV; or as direct reading ammeter of 10-0-10 A and as a direct reading voltmeter of 50-0-50 V. | |||
|
School Spano |

|
||
|
Function Measure of electric currents. | |||
|
|||
|
Description A helical spring holds a conic nucleus made of a thin plate of iron. This controls a long equilibrated index. It is suspended in proximity of the axe of a bobbin. When the current passes the nucleus is sucked inside, and the shift is proportional to the intensity of the current. The two ends of the coil end at the terminals fixed on the base, and the left terminal can be put in communication with a resistance placed in parallel on the circuit of the bobbin. If the current travels only in the latter, we read the upper scale (0 - 2) A; if the current bifurcates, the indications of the instrument are multiplied by five (and at that moment we must read the lower scale 0-10 A). In this second case, in fact, only a fifth of the current crosses the coil. | |||
|
School Spano |

|
||
|
Function Measure of potential differences. | |||
|
|||
|
Description The coil has an end united to the right terminal, while the other side ends on a plate of brass that can be connected to the left terminal. Between the plate and the terminal a bobbin is inserted, the resistance of which is four times that of the coil. If that resistance is excluded, the current travels only in the coil and the upper scale provides the indications. If we take the plug off, the total resistance becomes five times that of the coil and the indications must be multiplied by five (lower scale). | |||
|
School University |

|
||
|
Function To measure the intensity of current and the difference of potential. | |||
|
|||
|
School University |

|
||
|
Function To measure the intensity of current and the difference of potential. | |||
|
|||
|
School Spano |

|
||
|
Function Measuring the radiant energy. | |||
|
|||
|
Description It is based on the variation of the electric resistance of an iron darkened grating, subjected to the heating radiations. The variations of the resistance are measured with the method of the bridge. The apparatus is indispensable for the examination of the thermal propriety of the spectrum. | |||